PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS
Do NOT begin the exam until asked to do so.
There are 11 numbered pages and a periodic table in this exam. Check to see that they are all here before you begin the exam. Return all these papers when you are finished. Write your name on every page. Use a pen with blue or black ink for the entire exam.
Be sure to follow all directions. In working any numerical problem, you MUST SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. No credit will be given unless all work is clearly shown and the method of solution is logically correct. Pay attention to units and significant figures throughout.
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION MAY BE USEFUL
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
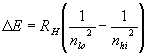
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Do not write below this line
Grader
(40) __________ __________
(40) __________ __________
(45) __________ __________
(25) __________ __________
BONUS (15) __________ __________
TOTAL (150) __________ __________ __________ __________
(40 points)
(14 points) Answer the questions on the blanks provided.
__________ 1. Consider the quantum number ℓ = 3 with the letter designation f. What is the maximum number of electrons in a 5f sublevel.
__________ 2. Write the symbol for most electronegative atom.
__________ 3. Which of the three species is the largest?
Na, Na+, S
__________ 4. Write the symbol for the ion in Group 2 that is isoelectronic to Cℓ-.
__________ 5. Write the abbreviated electron configuration for V2+.
__________ 6. Write the complete (unabbreviated) orbital diagram for O (oxygen). (Make sure you label all the orbitals)
__________ 7. Light emitted by an n = 4 to n = 2 transition will have same magnitude of energy that of from light emitted by an n=5 to n = 2 transition. (Y or N)
(2 points) State which of the following sets of quantum numbers would be possible (P) and which would be impossible (IP) for an electron in an atom.
n = 0, ℓ = 0, mℓ = 0, ms = + ½ ___________________________
n = 2, ℓ = 1, mℓ = -1, ms = + ½ ___________________________
(6 points) Classify each of the following species according to charge [neutral (N), anion (A), or cation (C)] and state [ground (G), excited (E), or impossible (IP)]:
Species |
Designation |
Charge |
State |
|
H |
1s1 |
|
|
|
O |
1s2 2s2 2p6 |
|
|
|
Na |
1s2 2s2 2p53s1 |
|
|
(10 points) Write the electron configuration and orbital diagram for Sn (tin, atomic number = 50) in its ground state. Answer the following questions and write your answers on the blanks provided. (The electron configuration and orbital diagram will not be graded).
_____________ 1. What is the highest value for n in the electron configuration?
_____________ 2. How many unpaired electrons are there?
_____________ 3. What is the highest value for mℓ in the configuration for Sn?
_____________ 4. How many electrons with ℓ = 1 does Sn4+ in its ground state have?
_____________ 5. How many electrons are in a d sublevel for the Sn4+ ion?
F. (8 points) Light with a wavelength of 465 nm lies in the blue region of the visible spectrum. (You might need this information 1nm = 1x 10-9 m)
Calculate the frequency of this light.
_______________________
Calculate the energy in kilojoules, of a mole of such photons.
_______________________
(40 points)
(10 points) Answer the questions below, using Y if the statement is true and N if the statement is false. Write your answers to blanks provided.
__________ 1. In order to form a covalent bond, an electron pair must be shared.
__________ 2. In the molecule XeF2 there are 2 sigma bonds and two unshared electron pairs around the central atom.
__________ 3. In the molecule ClF5, Cl is sp3d2 hybridized.
__________ 4. BeF2 is an exception to the octet rule.
__________ 5. A molecule that has a central atom with 4 covalent bonds and one unshared pair of electrons has a square planar geometry.
(6 points) Indicate whether each of the following statements about NO3- and its Lewis structure (given below) is true (Y) or false (N)
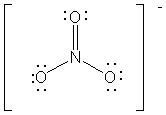
__________ 1. The O – N – O bond angles are all 120º.
__________ 2. The hybridization of N is sp3d.
__________ 3. Three different, valid resonance structures can be written for this molecule.
C. (5 points) Consider the molecule IBr2F where the first atom is the central atom. Draw their Lewis structure and use it to answer the questions below. (The Lewis structure will not be graded)
IBr2F
What is the total number of valence electrons? __________
How many bonds are there around the central atom? __________
How many unshared pairs are there around the central atom? __________
What is the molecular geometry around the central atom? __________
What are the ideal bond angles? __________
D. (8 points) Consider the following molecules whose molecular geometry is given. In the box provided, write P for polar, and NP for nonpolar.
|
|
|
|
|
|
linear |
tetrahedral |
square pyramidal |
octahedral |
|
|
|
|
|
E. (4 points) Consider the molecules shown below.
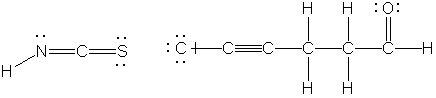
Number of σ- bonds ________ _______
Number of π- bonds ________ _______
F. (7 points) Below are the two different Lewis structures for nitrous acid (HNO2).
|
Structure I |
Structure II |
|
|
|
Calculate the formal charges for all atoms in each structure.
|
Structure I |
Structure II |
|
N ___________ Oa ___________ Ob ___________ |
N ___________ Oa ___________ Ob ___________ |
According the formal charges, which structure is more stable? ______________________
(45 points)
(15 points) Answer the questions below, using LT (for is less than), GT (for is greater than), EQ (for is equal to), or MI (for more information required) in the blanks provided.
Consider the reaction
3 A2 (ℓ) + XY3 (s) → X (s) + 3 A2Y (s) ∆Hº = 150 kJ
where A2 and X are elements in their native states. For this reaction:
__________ 1. The enthalpy of products (1) the enthalpy of reactants.
__________ 2. ∆Hfº for A2 (ℓ) (2) 0.
__________ 3. If ∆Hfº for A2Y = -70 kJ, ∆Hfº for XY3 (3) 80 kJ/mol.
__________ 4. If the heat absorbed by this reaction is given off by 1000 g of water, the change in temperature for the water is (4) 0.0359 ºC (to 3 significant figures).
__________ 5. ∆Hº for the reaction
1/3 X (s) + A2Y (s) → A2 (ℓ) + 1/3 XY3 (s)
(5) -50 kJ.
(5 points) Consider the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate.
2NaHCO3 (s) → Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (ℓ) + CO2 (g)
Using the following standard heats of formation:
|
NaHCO3 |
Na2CO3 |
H2O (ℓ) |
H2O (g) |
CO2 |
|
-947.7 kJ/mol |
-1130.8 kJ/mol |
-285.8 kJ/mol |
-241.8 kJ/mol |
-393.5 kJ/mol |
What is ∆Hº for the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate?
__________________
(15 points) When 7.50 g of a compound X decomposes, the temperature of a calorimeter (C = 9.33 kJ/ºC) increases by 4.83 ºC.
Is the reaction exothermic?
_______________
What is q for the decomposition?
_______________
What is q for the decomposition if 25.0 g of X decomposes?
_______________
What mass of X is required to raise the temperature of the calorimeter by 10.0ºC?
_______________
In another experiment, 2.45 kJ of heat evolved by the decomposition is absorbed by 65.0 g of water (specific heat = 4.18 J/g·ºC) at 25ºC. What is the final temperature of water?
_______________
(10 points) When propane gas is burned in air, the following reaction takes place:
C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (ℓ) ∆Hº = -2219.9 kJ
How much heat is evolved when 10.0 g of C3H8 (MM = 44.1 g/mol) burns in excess oxygen?
__________________
What volume of CO2 at 1.00 atm and 27 ºC is liberated when 1000.0 kJ of heat is evolved?
__________________
(25 points)
(14 points) Three compounds, X, Y, Z can act as oxidizing agents. In solution, X is green, Y is yellow and Z is red. In the reactions in which they participate, they are reduced to X-, Y-, Z- ions, all of which are colorless.
When a solution of X is mixed with a solution of Z- ions, the color changes from green to red.
Which species is oxidized? _______________
Which species is reduced? _______________
Is X a better oxidizing agent than Z? _______________
When a solution of X is mixed with a solution containing Y- ions, the color remains green.
Is X a better oxidizing agent than Y? _______________
Arrange X, Y and Z in order of increasing strengths as oxidizing agents.
__________ < __________ < ___________
(11 points) To determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid, we vaporize the liquid in a flask of known volume, then condense the liquid and determine the mass of condensed liquid. Given the following data, answer the questions below:
|
Mass of flask and cap |
56.561 g |
|
Mass of flask, cap and condensed liquid |
57.085 g |
|
Barometric pressure |
752 mm Hg |
|
Temperature of hot water bath |
98 ºC |
|
Volume of the flask |
278 mL |
What is the mass of the condensed liquid?
_______________
How many moles of gas are in the flask at 98 ºC and 752 mm Hg?
_______________
What is the molar mass of the liquid?
_______________
The bonus should be done only after you have completed the main part of this exam and the checked your work for errors. The time allotted for this exam does not include time for the bonus. (SHOW ALL WORK!) Wild guesses will not be considered.
Consider the following reaction:
2Al (s) + Cr2O3 (s) → Al2O3 (s) + 2Cr (s)
By using the table given below, calculate the temperature to which the products of the reaction will be raised, starting from room temperature (25ºC), by the heat given off by the reaction.
|
|
Standard enthalpy of formation (kJ/mol) |
Specific heat (J/g·ºC) |
|
Al2O3 (s) |
-1675.7 |
0.77 |
|
Cr2O3 (s) |
-1139.7 |
|
|
Cr (s) |
|
0.45 |